Step-by-Step Implementation of Our Form Validation App
Step-by-Step Implementation of Our Form Validation App
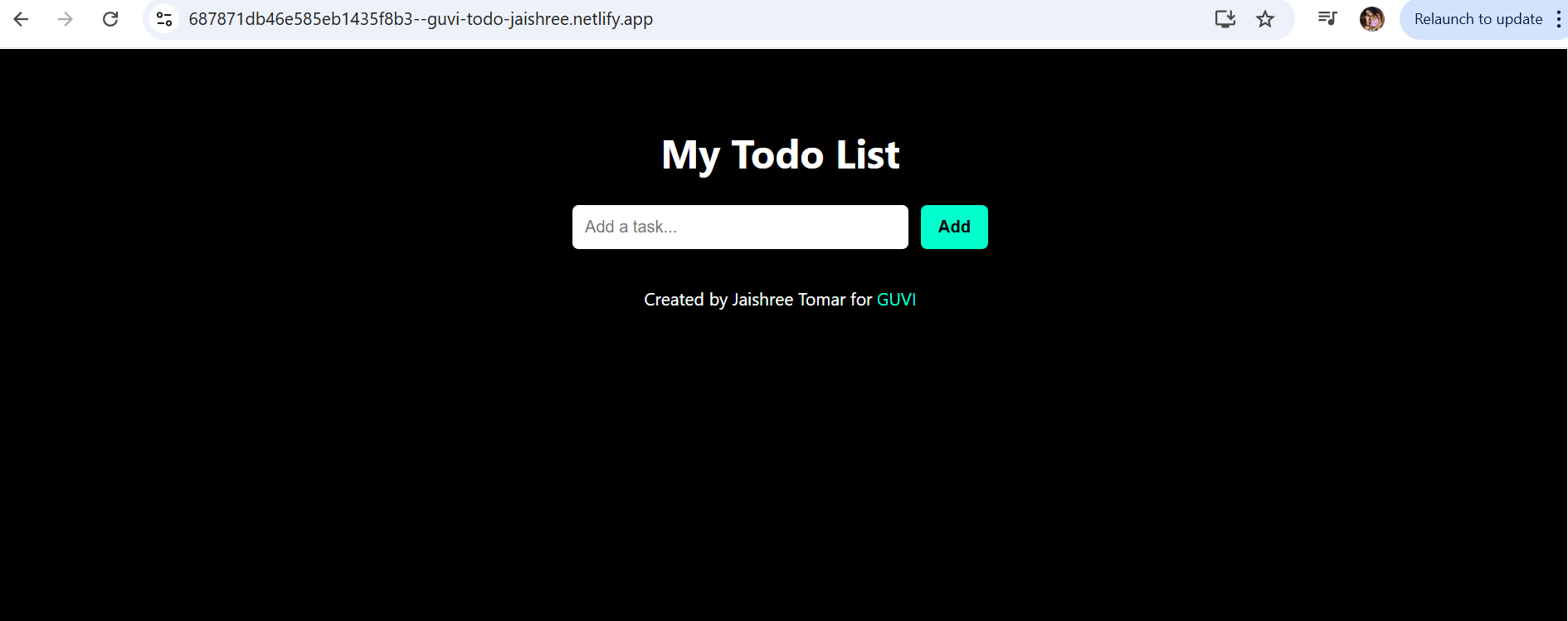
In this module, we’ll actually build the Form Validation app. We’ll set up the project with Vite, organize the structure, add the form with validation, connect it to the hobby dataset, and style it neatly.
1) Set up the environment
We’ll use Vite for a fast React environment.
Open your terminal and run:
npm create vite@latest form-validation-app
Choose the following options:
- Project name: form-validation-app
- Framework: React
- Variant: JavaScript
Next, install dependencies:
cd form-validation-app
npm install
Start the development server:
npm run dev
You’ll see a local URL like http://localhost:5173/. Open it in your browser. The Vite + React starter page will appear.
2) Create Application Structure (Directory Structure)
After running Vite, you’ll get this structure:
form-validation-app/
├── index.html
├── package.json
├── vite.config.js
├── public/
│ └── hobbies.json
└── src/
├── App.jsx
├── App.css
├── index.css
└── main.jsx
- index.html: contains <div id="root"></div>. React injects our app here.
- src/main.jsx: entry point that renders <App />.
- src/App.jsx: main component where we build the form logic.
- src/App.css and src/index.css: styling files.
- public/hobbies.json: dataset of hobbies and tags we’ll use to generate suggestions.
3) Rendering App in main.jsx
Open src/main.jsx. By default, it looks like this:
import { StrictMode } from 'react'
import { createRoot } from 'react-dom/client'
import './index.css'
import App from './App.jsx'
createRoot(document.getElementById('root')).render(
<StrictMode>
<App />
</StrictMode>,
)
This code finds the root div in index.html and renders the <App /> component into it.
4) Building the Form in App.jsx
Now open src/App.jsx and replace it with our form logic.
Step 1: Import React and CSS
import React, { useState, useEffect } from "react";
import "./App.css";
Step 2: Define state
We’ll store:
- formData: user’s name and interests
- dataset: hobbies loaded from hobbies.json
- suggestions: suggested hobbies after form submission
const [formData, setFormData] = useState({ name: "", interests: "" });
const [dataset, setDataset] = useState([]);
const [suggestions, setSuggestions] = useState([]);
Step 3: Load hobbies.json
When the app starts, we fetch the hobby dataset from the public folder:
useEffect(() => {
fetch("/hobbies.json")
.then((res) => res.json())
.then((data) => setDataset(data));
}, []);
Step 4: Handle input changes
function handleChange(e) {
const { name, value } = e.target;
setFormData(prev => ({ ...prev, [name]: value }));
}
Step 5: Handle form submission
On submit, we split the user’s interests, match them with the dataset, and generate suggestions.
function handleSubmit(e) {
e.preventDefault();
const interestsArray = formData.interests
.split(",")
.map(i => i.trim().toLowerCase());
const suggested = generateSuggestions(interestsArray, dataset);
setSuggestions(suggested);
}
Step 6: Suggestion logic
We give each hobby a score based on matched tags, then return the top 10 results.
function generateSuggestions(interests, dataset) {
let scoredHobbies = {};
dataset.forEach(item => {
let score = 0;
item.tags.forEach(tag => {
interests.forEach(interest => {
if (tag.toLowerCase().includes(interest)) score += 1;
});
});
if (score > 0) scoredHobbies[item.hobby] = score;
});
let sortedHobbies = Object.entries(scoredHobbies)
.sort((a, b) => b[1] - a[1])
.map(entry => entry[0]);
return sortedHobbies.length
? sortedHobbies.slice(0, 10)
: ["Try exploring new hobbies like reading, coding, music, or fitness!"];
}
Step 7: Return the UI
return (
<div className="app">
<main className="main">
<h1>Hobby Suggestion Form</h1>
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit} className="form-container">
<input
type="text"
name="name"
value={formData.name}
onChange={handleChange}
placeholder="Your Name"
required
/>
<input
type="text"
name="interests"
value={formData.interests}
onChange={handleChange}
placeholder="Your Interests (comma-separated)"
required
/>
<button type="submit">Suggest Hobbies</button>
</form>
{suggestions.length > 0 && (
<div className="suggestions-container">
<h3>Suggested Hobbies:</h3>
<ul>
{suggestions.map((s, i) => (
<li key={i}>{s}</li>
))}
</ul>
</div>
)}
</main>
<footer>
Made by <strong>Your Name</strong>
</footer>
</div>
);
5) Styling with CSS
We use App.css to style the form and suggestion list.
- The page has a dark gradient background.
- The form is styled like a card with shadows and rounded corners.
- Inputs glow when focused.
- The suggestion list fades in smoothly with animation.
Example:
.form-container {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
gap: 16px;
background: #1f1f2e;
padding: 30px 25px;
border-radius: 16px;
max-width: 500px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
6) Final Touches and Deployment
- Add a footer with your name or link.
- Test by entering your name and some interests (like "coding, music").
The app will suggest hobbies such as "Build a React App" or "Play Guitar".
To deploy, build the app:
npm run build
- This creates a dist/ folder with optimized files.
You can host it easily on Netlify or Vercel by dragging and dropping the dist/ folder. Now the app is complete. It takes user input, validates it, matches it against the dataset, and shows personalized hobby suggestions in a clean UI.