Conclusion of the Project
Conclusion
Kudos to you! You’ve successfully built and deployed your first weather application with React. In this final module, we’ll reflect on what you’ve accomplished, share a live demo link, test your understanding with quick MCQs, and guide you to resources to continue your learning.
Learning Outcomes
By completing this project, you’ve learned and applied several core front-end development concepts. Here's what you’ve achieved:
- Set up a React project: You created a weather app using Create React App, configured your folder structure, and managed dependencies like react, react-dom, and npm.
- Built reusable components: You created modular and reusable components such as SearchBar, WeatherCard, and TimeDisplay using functional components and props.
- Used React Hooks: You used the useState and useEffect hooks for state management and real-time updates like the live clock.
- Fetched API data and handled errors: You called OpenWeatherMap’s API dynamically based on the user's input and handled success and failure states with loading messages and error handling.
- Styled with CSS and animations: You applied custom styles and transitions using App.css and WeatherCard.css, including smooth hover effects and animations.
- Deployed using Vercel: You deployed the app for free using Vercel, allowing anyone to access your live weather checker on the web.
You now have the essential skills to build, style, and deploy modern interactive apps using React.
Live Link & Output Screenshot
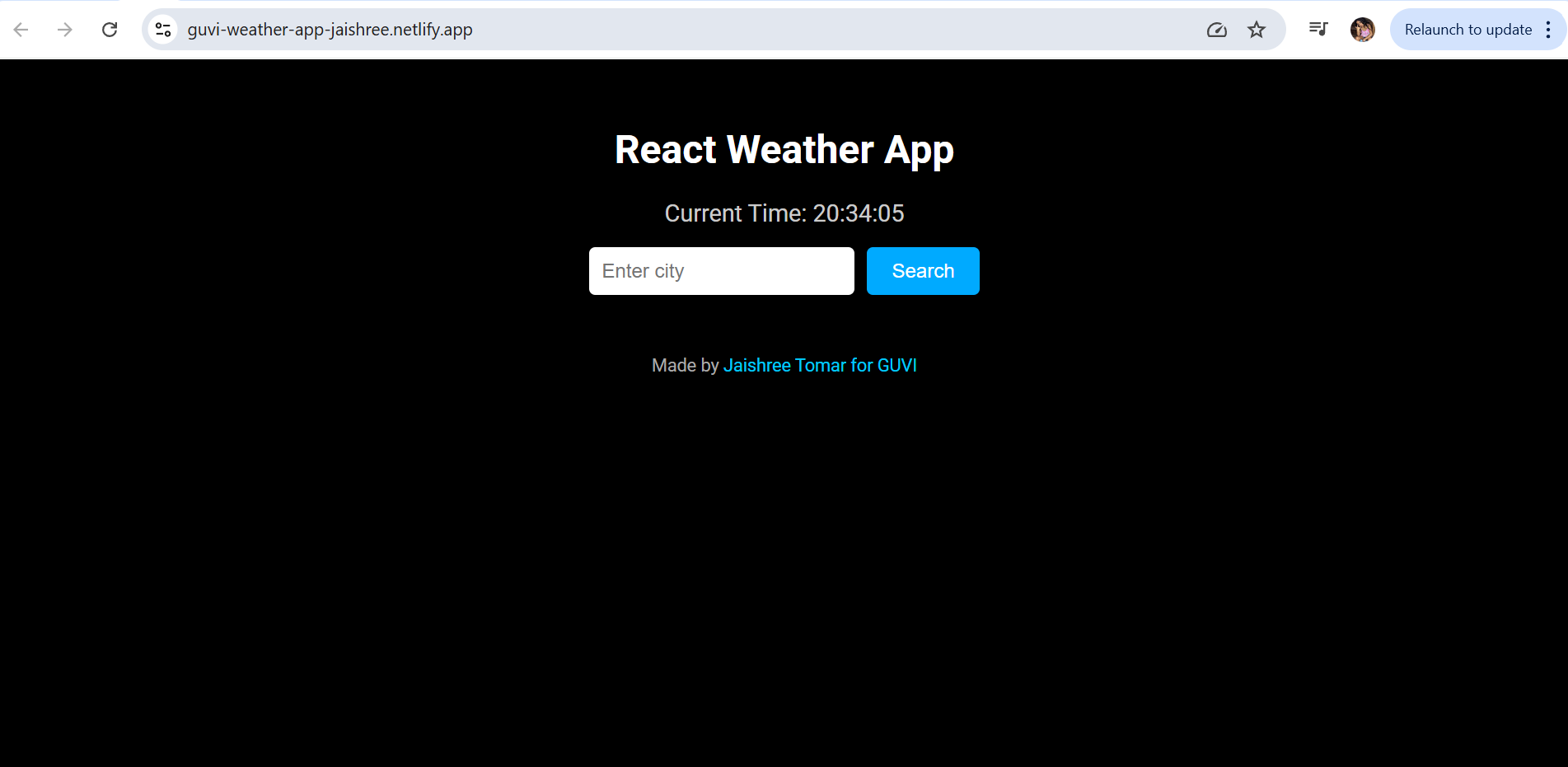
Live Demo: React GUVI Weather App
This is how your final app should look after deployment:
MCQs (Answers at the end)
1. Which React Hook lets you store and update state in functional components?
a. useEffect
b. useReducer
c. useState
d. useContext
2. What is the purpose of the useEffect hook in the TimeDisplay component?
a. Handle user input
b. Perform side-effects like setting intervals
c. Add CSS styles
d. None of the above
3. What happens if the city entered is not found?
a. App crashes
b. Nothing happens
c. A default city is shown
d. An error message is displayed
4. Why do we include setLoading(true) and setLoading(false) in handleSearch?
a. To show a loading spinner or message during fetch
b. To prevent React errors
c. To avoid rendering
d. To style the app
5. What is the primary role of SearchBar.js?
a. Display the temperature
b. Render the weather card
c. Accept user input and pass it to the parent
d. Call the weather API directly
Answer Key:
Question | Answer | Explanation |
| Q1 | a | useState is a React Hook that lets you add state to functional components. It returns an array with two elements: the state and the function to update it. |
| Q2 | b | getWeatherByCity is an async function, so await is necessary to pause execution until it returns the fetched weather data. |
| Q3 | c | The condition {weatherData && <WeatherCard data={weatherData} />} ensures the component renders only when weatherData has a truthy value. |
| Q4 | c | The onSearch prop in SearchBar is a function, which is invoked in SearchBar using onSearch(city) when the user submits a city. |
| Q5 | b | The footer uses an anchor tag (<a>) to link to GUVI's website and includes attributes target="_blank" and rel="noreferrer" for safe new-tab behavior. |
Resources
Ready to take your React skills even further? Here are some curated resources to help you continue building amazing apps:
1) GUVI’s ReactJS Self-Paced Course
Want to master React from the ground up and build more portfolio projects? Check out GUVI’s ReactJS Course where you will:
- Learn components, routing, forms, hooks, and more
- Build real-world apps with guided mentorship
2) Full Stack Development Path
Want to build full apps — including frontend, backend, and database? Then check out GUVI’s IIM-M Pravartak Certified Full Stack Development Course that covers:
- React (Frontend)
- Node.js & Express (Backend)
- MongoDB (Database)
- Version Control, Deployment & More
Perfect for beginners ready to launch a full-fledged web development career.
Final Words
You’ve built and deployed a live weather app—complete with animations, live data, error handling, and responsive design. You've not only learned how React works but also how to think like a developer by breaking the app into modular components and managing state effectively.
Keep building, keep learning—and keep shipping cool projects to the web! Good Luck!